EvolutionaryScale
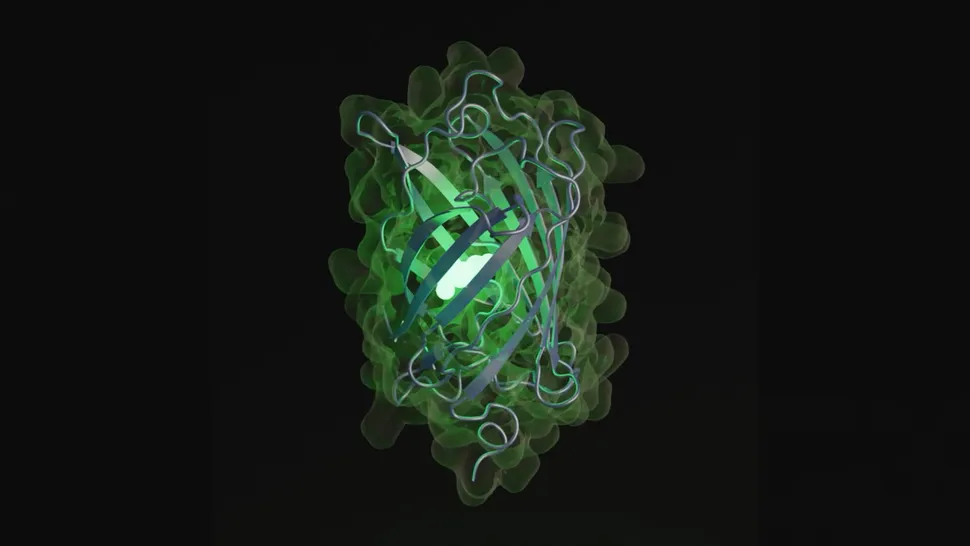
An artificial intelligence (AI) model has simulated half a billion years of molecular evolution to create the code for a previously unknown protein, according to a new study. The glowing protein, which is similar to those found in jellyfish and corals, may help in the development of new medicines, researchers say. Proteins are one of the building blocks of life and perform various functions in the body, such as building muscles and fighting disease……Continue reading…..
By:
Source: Live Science
.
Critics:
The science of molecules is called molecular chemistry or molecular physics, depending on whether the focus is on chemistry or physics. Molecular chemistry deals with the laws governing the interaction between molecules that results in the formation and breakage of chemical bonds, while molecular physics deals with the laws governing their structure and properties. In practice, however, this distinction is vague.
In molecular sciences, a molecule consists of a stable system (bound state) composed of two or more atoms. Polyatomic ions may sometimes be usefully thought of as electrically charged molecules. The term unstable molecule is used for very reactive species, i.e., short-lived assemblies (resonances) of electrons and nuclei, such as radicals, molecular ions, Rydberg molecules, transition states, van der Waals complexes, or systems of colliding atoms as in Bose–Einstein condensate.
Molecules as components of matter are common. They also make up most of the oceans and atmosphere. Most organic substances are molecules. The substances of life are molecules, e.g. proteins, the amino acids of which they are composed, the nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), sugars, carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins. The nutrient minerals are generally ionic compounds, thus they are not molecules, e.g. iron sulfate.
However, the majority of familiar solid substances on Earth are made partly or completely of crystals or ionic compounds, which are not made of molecules. These include all of the minerals that make up the substance of the Earth, sand, clay, pebbles, rocks, boulders, bedrock, the molten interior, and the core of the Earth. All of these contain many chemical bonds, but are not made of identifiable molecules.
No typical molecule can be defined for salts nor for covalent crystals, although these are often composed of repeating unit cells that extend either in a plane, e.g. graphene; or three-dimensionally e.g. diamond, quartz, sodium chloride. The theme of repeated unit-cellular-structure also holds for most metals which are condensed phases with metallic bonding. Thus solid metals are not made of molecules.
In glasses, which are solids that exist in a vitreous disordered state, the atoms are held together by chemical bonds with no presence of any definable molecule, nor any of the regularity of repeating unit-cellular-structure that characterizes salts, covalent crystals, and metals. Molecules are generally held together by covalent bonding. Several non-metallic elements exist only as molecules in the environment either in compounds or as homonuclear molecules, not as free atoms: for example, hydrogen.
While some people say a metallic crystal can be considered a single giant molecule held together by metallic bonding, others point out that metals behave very differently than molecules. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are termed shared pairs or bonding pairs, and the stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms, when they share electrons, is termed covalent bonding.
Most molecules are far too small to be seen with the naked eye, although molecules of many polymers can reach macroscopic sizes, including biopolymers such as DNA. Molecules commonly used as building blocks for organic synthesis have a dimension of a few angstroms (Å) to several dozen Å, or around one billionth of a meter. Single molecules cannot usually be observed by light (as noted above), but small molecules and even the outlines of individual atoms may be traced in some circumstances by use of an atomic force microscope.
Some of the largest molecules are macromolecules or supermolecules. The smallest molecule is the diatomic hydrogen (H2), with a bond length of 0.74 Å. Effective molecular radius is the size a molecule displays in solution. The table of permselectivity for different substances contains examples. The chemical formula for a molecule uses one line of chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to one typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts.
A compound’s empirical formula is a very simple type of chemical formula. It is the simplest integer ratio of the chemical elements that constitute it. For example, water is always composed of a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms, and ethanol (ethyl alcohol) is always composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 2:6:1 ratio. However, this does not determine the kind of molecule uniquely – dimethyl ether has the same ratios as ethanol, for instance. Molecules with the same atoms in different arrangements are called isomers.
Also carbohydrates, for example, have the same ratio (carbon:hydrogen:oxygen= 1:2:1) (and thus the same empirical formula) but different total numbers of atoms in the molecule. The molecular formula reflects the exact number of atoms that compose the molecule and so characterizes different molecules. However different isomers can have the same atomic composition while being different molecules.
The empirical formula is often the same as the molecular formula but not always. For example, the molecule acetylene has molecular formula C2H2, but the simplest integer ratio of elements is CH. The molecular mass can be calculated from the chemical formula and is expressed in conventional atomic mass units equal to 1/12 of the mass of a neutral carbon-12 (C isotope) atom. For network solids, the term formula unit is used in stoichiometric calculations.
Molecules have fixed equilibrium geometries—bond lengths and angles— about which they continuously oscillate through vibrational and rotational motions. A pure substance is composed of molecules with the same average geometrical structure. The chemical formula and the structure of a molecule are the two important factors that determine its properties, particularly its reactivity. Isomers share a chemical formula but normally have very different properties because of their different structures.
Stereoisomers, a particular type of isomer, may have very similar physico-chemical properties and at the same time different biochemical activities. Molecular spectroscopy deals with the response (spectrum) of molecules interacting with probing signals of known energy (or frequency, according to the Planck relation). Molecules have quantized energy levels that can be analyzed by detecting the molecule’s energy exchange through absorbance or emission.
Spectroscopy does not generally refer to diffraction studies where particles such as neutrons, electrons, or high energy X-rays interact with a regular arrangement of molecules (as in a crystal). Microwave spectroscopy commonly measures changes in the rotation of molecules, and can be used to identify molecules in outer space. Infrared spectroscopy measures the vibration of molecules, including stretching, bending or twisting motions. It is commonly used to identify the kinds of bonds or functional groups in molecules.
Changes in the arrangements of electrons yield absorption or emission lines in ultraviolet, visible or near infrared light, and result in colour. Nuclear resonance spectroscopy measures the environment of particular nuclei in the molecule, and can be used to characterise the numbers of atoms in different positions in a molecule.





Leave a Reply